Probing the superconducting pairing of the La4Be33Pt16 alloy via muon-spin spectroscopy
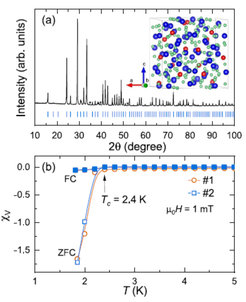
We report a study of the superconducting pairing of the noncentrosymmetric La4Be33Pt16 alloy using muon-spin rotation and relaxation (µSR) technique. Below Tc=2.4 K, La4Be33Pt16 exhibits bulk superconductivity (SC), here characterized by heat-capacity and magnetic-susceptibility measurements. The temperature dependence of the superfluid density ρsc(T), extracted from the transverse-field µSR measurements, reveals a nodeless SC in La4Be33Pt16. The best fit of ρsc(T) using an s-wave model yields a magnetic penetration depth λ0=542 nm and a superconducting gap Δ0=0.37 meV at zero Kelvin. The single-gapped superconducting state is further evidenced by the temperature-dependent electronic specific heat Ce(T)/T and the linear field-dependent electronic specific-heat coefficient γH(H). The zero-field µSR spectra collected in the normal- and superconducting states of La4Be33Pt16 are almost identical, confirming the absence of an additional field-related relaxation and, thus, of spontaneous magnetic fields below Tc. The nodeless SC combined with a preserved time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state proves that the spin-singlet pairing is dominant in La4Be33Pt16. This material represents yet another example of a complex system showing only a conventional behavior, in spite of a noncentrosymmetric structure and a sizeable spin–orbit coupling.












